[Micro Science Popularization] How to improve sleep disorders in the elderly through diet?
In recent years, many elderly people have taken the initiative to visit the nutrition department, looking forward to improving symptoms of fatigue, or solving problems such as poor sleep quality. Some elderly people try to drink milk before going to bed, take a bath, do not drink tea drinks, do not discuss problems and other ways, the effect is not significant, hoping to improve sleep through dietary ways.
First, the related factors of insomnia
As a kind of disease, the pathogenesis of insomnia is currently thought to be mainly related to the abnormal gamma-aminobutyric neuronal system, central neurotransmitter disorder, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA axis) function disorder, the influence of inflammatory response factors, melatonin function decline, sympathetic hyperactivity.
The related influencing factors of insomnia also include the influence of chronic diseases such as hypertension and diabetes, and there are exact studies that show that various mechanisms of the formation of hypertension have a greater impact on sleep. In addition to the above reasons, physiological, psychological, environmental, drug, diet and other factors and bad habits before going to bed, tobacco, alcohol and tea habits are also important factors affecting the quality of sleep of patients.
Second, the definition and role of γ-aminobutyric acid
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), is a natural presence in the human body, non-protein composition of active amino acid neurotransmitter, 30% of human brain neurons contain GABA, almost affects all neural activities, has a neuroprotective effect, can play hypnosis, sedation and anti-anxiety, improve brain function, reduce blood pressure and other functions. It slows down the brain by blocking specific signals in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). The inhibition of GABA in the peripheral blood system of insomnia patients is impaired, which may be related to the abnormal expression of its receptor subunits. Therefore, GABA is believed to have the effect of reducing stress, relieving anxiety, as well as improving sleep, and its reduction can lead to anxiety and mood disorders, schizophrenia, autism spectrum disorders, and depression.
3. Gamma-aminobutyric acid deficiency and food sources
GABA is a substance that the body naturally secretes, but with age and stress, GABA secretion continues to decrease, resulting in a decline in sleep quality. Studies have shown that people with insomnia secrete 30% less GABA than normal people. And the amount of GABA secreted by the body drops by about 5% every 10 years, with women falling faster.
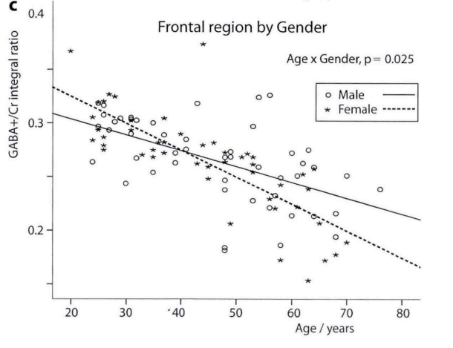
(Photo 1, Credit: Goofy. Study on the correlation between brain GABA content and age in normal population by magnetic resonance spectroscopy [D]. Shandong: Shandong University,2012.)
GABA is an amino acid found in vegetables, fruits and fermented foods, such as pickles, fermented foods such as tempeh, and green, black and oolong teas. Other foods that contain GABA or promote its production in the body include brown rice, soybeans and red beans, chestnuts, mushrooms, tomatoes, spinach, broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, sprouted grains, and sweet potatoes. Common foods with relatively high GABA content are pumpkin, lychee and longan.

(Photo 2, source: Internet)
As the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, GABA has a wide range of biological activities. Therefore, functional foods rich in GABA are widely sought after by consumers. However, the amount of GABA in natural foods is usually low and does not meet people's needs for health effects. With increasing public awareness of food safety and natural processes, the use of enrichment techniques to increase GABA content in food, rather than exogenous additions, could improve acceptability among health-conscious consumers.
Fourth, dietary guidance for sleep disorders in the elderly
Recently, the Chinese Nutrition Society issued the "Dietary Guidance for Sleep disorders in the elderly" group standard (draft for comment). The elderly can improve their sleep in the following ways:
1. The dietary guidance provides dietary nutritional supplement recommendations for the sleep disorders of the elderly:
(1) gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) supplements can be appropriately supplemented.
(2) Probiotics can be appropriately supplemented, such as Lactobacillus brevis and bifidobacterium longum.
(3) Iron, zinc, magnesium, copper and other trace element supplements can be taken in appropriate amounts.
(4) DHA and EPA can be appropriately supplemented.
(5) B vitamin supplements can be taken appropriately.
(6) Appropriate use of vitamin D supplements. Or sunshine 3-4 times a week, 20-30min each time.
2. Food choices:
(1) Can increase the intake of fresh, tender, loose and soft food types;
(2) Increase the intake of medicinal and edible homologous foods such as jujube kernel, jujube and lily;
(3) Increase intake of foods rich in melatonin, such as cherries, bananas, tomatoes, cucumbers, nuts and multigrain cereals;
(4) Increase the intake of natural GABA-rich foods, such as pumpkin, lychee, longan, green tea, mulberry, etc.;
Limit alcohol intake, especially in the hours before bed;
(6) Avoid spicy food at dinner or before bed;
(7) Limit the intake of stimulants such as coffee, tea, chocolate and carbonated beverages.
3. Cooking methods recommend cooking methods such as steaming, stewing soup and porridge, and avoid braising, frying, frying, roasting and barbecuing food.
4. In terms of meal time, it is recommended to eat breakfast regularly, dinner time should be no later than 3 hours before going to bed, and dinner energy intake accounts for 25%-30% of the total energy of the day. Avoid excessive eating at night, high-sugar or high-fat food, if you do need to eat, you can choose to eat a small amount of non-stimulating and easy to digest food half an hour or 1 hour before going to bed, such as white porridge, noodles, etc.
5. Lifestyle aspects related to proper diet.
(1) Maintain a stable routine of life, including meal time, bedtime and wake up time;
(2) Create a good living atmosphere, encourage the elderly to make, share food and eat together, and create a warm and pleasant dining environment and atmosphere;
(3) Improve the flavor and color of food by improving reasonable cooking methods;
(4) Monitoring body weight, body mass index is suitable for 20-26.9kg/m2, should often carry out dietary guidance and sleep assessment;
(5) Regular and moderate exercise, it is recommended that morning, afternoon and evening activities are half an hour each day, exercise more than 3 times a week;
(6) Suggestions to increase guidance on improving psychological problems.
It is important to note that individual differences and special needs of older adults may vary. If you have specific questions about eating and sleeping, it is recommended to consult a dietitian or doctor for further guidance and advice tailored to your individual needs.
References:


